"In the realm of JavaScript's code,
Variables hold a powerful mode."
In JavaScript, variables are used to store data values.
Variable Declaration:
In JavaScript, you can declare variables using the var, let, or const keywords.
Already discussed in the previous blog ( Link to it ).
1. Variable Naming:
- Variables can have a wide range of names, but they must follow certain rules:
- They can contain letters, digits, underscores, or the dollar sign.
- The first character must be a letter, an underscore, or a dollar sign.
- Variables are case-sensitive (myVariable and myvariable are considered different variables).
- It's a good practice to use descriptive names that reflect the purpose of the variable.
JavaScript has a set of reserved keywords that have predefined meanings and cannot be used as identifiers (such as variable names or function names) in your code.
2. Variable Assignment:
- You can assign a value to a variable using the assignment operator (=).
- The assigned value can be a number, string, boolean, array, object, or any other valid JavaScript data type.
3. Variable Reassignment:
- Once a variable is declared, you can update its value by assigning a new value to it.
- Variables declared with let can be reassigned with a new value, while variables declared with const are read-only and cannot be reassigned.
4. Variable Scope:
- The scope of a variable determines where it is accessible within your code.
- Variables declared with var have function-level scope, meaning they are accessible within the function in which they are declared or globally if declared outside of any function.
- Variables declared with let and const have block-level scope, meaning they are accessible only within the block of code they are declared in (e.g., inside a loop or an if statement).
Supplementary Reading:
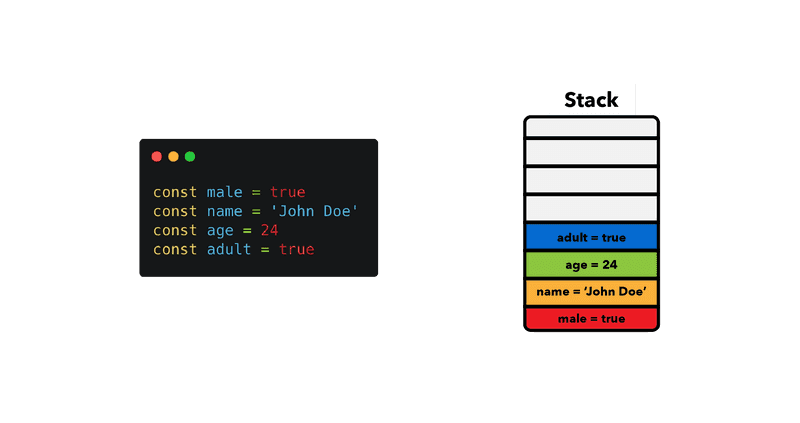
In JavaScript, variables are stored in memory during the execution of a program. The memory location where a variable's value is stored depends on the type of variable and its scope. Let's discuss how variables are stored in memory in JavaScript:
Primitive Data Types:
Variables that hold primitive data types (such as numbers, strings, booleans, null, and undefined) store the actual value directly in memory.
When you declare a variable and assign a primitive value to it, the value is stored in memory at the variable's memory location.

+in+JavaScript.jpg)
Comments
Post a Comment